INTRODUCTION
Terrorism and extremist violence represent significant threats to global security, stability, and human rights. These forms of violence are often driven by radical ideologies, political grievances, or religious fanaticism, aiming to instill fear, provoke social unrest, and advance ideological agendas. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll delve into the complexities of terrorism and extremist violence, exploring their root causes, impacts on societies, strategies for prevention and counteraction, and the role of international cooperation in addressing these threats.

1. Root Causes of Terrorism and Extremist Violence:
- Terrorism and extremist violence can stem from a combination of socio-economic factors, political grievances, religious radicalization, ethnic tensions, and geopolitical conflicts.
- Extremist groups exploit grievances, real or perceived injustices, and marginalized communities to recruit members, radicalize sympathizers, and justify acts of violence.
- Radical ideologies, including religious extremism, nationalist extremism, and supremacist beliefs, play a significant role in motivating individuals and groups to engage in acts of terrorism and violence.
2. Characteristics of Terrorism and Extremist Violence:
- Terrorism involves the deliberate use of violence, intimidation, or coercion to achieve political, ideological, or religious objectives, often targeting civilians, infrastructure, or symbols of authority.
- Extremist violence encompasses a wide range of tactics, including bombings, shootings, kidnappings, assassinations, cyberattacks, and propaganda campaigns aimed at spreading fear and propaganda.
- Terrorist organizations may operate clandestinely or openly, exploiting modern communication tools, social media platforms, and cyberspace to recruit, radicalize, and mobilize supporters.
3. Impacts of Terrorism and Extremist Violence:
- Terrorism and extremist violence inflict profound physical, psychological, and socio-economic harm on victims, communities, and societies at large.
- Attacks on civilians, public infrastructure, and critical facilities disrupt daily life, undermine trust in institutions, and create a climate of fear, anxiety, and insecurity.
- Terrorism can have far-reaching consequences, including loss of life, displacement of populations, destruction of property, economic disruptions, and social divisions, perpetuating cycles of violence and retaliation.
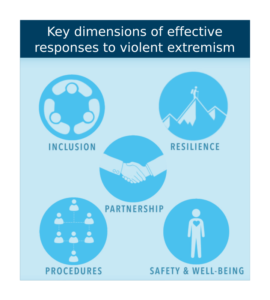
4. Strategies for Prevention and Counteraction:
- Preventing terrorism and extremist violence requires a comprehensive, multi-dimensional approach that addresses root causes, promotes social cohesion, and counters radicalization at the local, national, and international levels.
- Effective prevention strategies include community engagement, education, youth empowerment, deradicalization programs, and addressing socio-economic grievances that fuel extremism.
- Law enforcement agencies, intelligence services, and security forces play a crucial role in detecting, disrupting, and dismantling terrorist networks, interdicting extremist propaganda, and prosecuting perpetrators.

5. International Cooperation and Collaboration:
- Addressing the global threat of terrorism and extremist violence requires coordinated efforts, information sharing, and cooperation among governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector.
- Multilateral initiatives, such as the United Nations Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy, regional security alliances, and bilateral partnerships, facilitate joint action, capacity-building, and resource mobilization to combat terrorism and extremism.
- International legal frameworks, including conventions against terrorism, extradition treaties, and UN Security Council resolutions, provide mechanisms for cooperation, coordination, and collective action to counter transnational terrorist threats.
6. Protecting Human Rights and Rule of Law:
- Upholding human rights, democratic principles, and the rule of law is essential in the fight against terrorism and extremist violence, ensuring that counterterrorism measures respect due process, accountability, and non-discrimination.
- Counterterrorism policies should strike a balance between security imperatives and safeguarding civil liberties, freedom of expression, privacy rights, and minority rights, to prevent the erosion of democratic norms and values.
In conclusion, terrorism and extremist violence pose complex and multifaceted challenges that require comprehensive and collaborative responses from the international community. By addressing root causes, promoting social inclusion, strengthening security measures, and upholding human rights and the rule of law, stakeholders can mitigate the risks posed by terrorism and extremism and build resilient and cohesive societies resilient to violent ideologies.



