Introduction:
Immigration-related crimes and border security are pressing issues in the United States, drawing attention to the complexities of migration, law enforcement, and national security. This essay examines the various dimensions of immigration-related crimes, the challenges faced in securing the borders, and the implications for policy and society.
Understanding Immigration-Related Crimes:
Immigration-related crimes encompass a range of offenses associated with the movement of people across borders. These crimes may include illegal entry or reentry, human trafficking, smuggling of contraband, document fraud, and immigration fraud. While some offenses primarily involve migrants themselves, others may involve criminal organizations exploiting vulnerable individuals for profit.
Challenges in Securing the Borders:
Securing the borders of the United States presents multifaceted challenges:
1. Geographic Complexity:
The US shares borders with Canada and Mexico, spanning vast and diverse terrain, including remote deserts, rugged mountains, and dense forests. Policing such expansive and varied landscapes poses logistical challenges for border enforcement agencies.
2. Technological Limitations:
Despite advancements in surveillance technology, border security agencies still face limitations in monitoring and patrolling remote areas effectively. Smugglers and traffickers exploit gaps in surveillance to evade detection and transport contraband or individuals across the border.
3. Resource Constraints:
Adequately staffing and funding border security efforts require significant resources. Budgetary constraints and competing priorities may limit the capacity of border enforcement agencies to deploy personnel, infrastructure, and technology effectively.
Implications for Policy and Society:
The management of immigration-related crimes and border security has far-reaching implications for policy, society, and human rights:
1. Policy Debates:
Immigration policy debates often center on questions of border security, enforcement priorities, and pathways to legal status. Divergent political ideologies and interests shape policy decisions, leading to ongoing debates about the balance between security concerns and humanitarian considerations.
2. Humanitarian Concerns:
Stringent border enforcement measures can have humanitarian consequences, particularly for vulnerable populations such as asylum seekers, unaccompanied minors, and migrant families. Policies that prioritize deterrence over protection may exacerbate risks of exploitation, violence, and harm for those seeking refuge or better opportunities in the US.
3. International Relations:
Border security policies and practices can impact diplomatic relations with neighboring countries and international partners. Collaborative efforts to address transnational threats, such as drug trafficking or human smuggling, require cooperation and coordination among governments.
Impact of Immigration Enforcement Policies
Immigration enforcement policies adopted by the US government have significant implications for border security and immigration-related crimes:
Zero Tolerance Policy:
Policies such as the zero-tolerance approach, which seeks to prosecute all individuals crossing the border illegally, have led to an increase in criminal prosecutions for immigration-related offenses. However, critics argue that such policies can overwhelm the criminal justice system and exacerbate overcrowding in detention facilities.
Deportation Policies:
Aggressive deportation policies aimed at removing undocumented immigrants from the country can impact border security by deterring individuals from attempting unauthorized crossings. However, they may also drive migrants to resort to riskier methods, such as crossing through remote and dangerous areas, increasing their vulnerability to exploitation and harm.
Role of Technology in Border Surveillance
Advancements in technology play a crucial role in enhancing border surveillance and security:
Remote Sensing Technology:
Technologies such as radar, infrared cameras, and aerial drones enable border enforcement agencies to monitor remote and rugged terrain more effectively, detecting unauthorized crossings and illicit activities in real-time.
Biometric Identification:
Biometric screening technologies, including facial recognition and iris scanning, are increasingly used to verify the identity of individuals crossing the border and to detect fraudulent documents or identity theft.
Analytics:
Data analytics and predictive modeling tools help border enforcement agencies analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns of illegal activity, and deploy resources more efficiently to target high-risk areas and individuals.

Challenges of Addressing Human Rights Concerns
Balancing border security objectives with human rights considerations poses significant challenges:
Family Separation:
Policies that result in the separation of migrant families, such as the practice of detaining parents separately from their children, have raised concerns about the psychological and emotional impact on affected individuals, particularly children.
Asylum Processing:
Delays and backlogs in asylum processing can result in prolonged detention of asylum seekers, raising concerns about due process rights, access to legal representation, and conditions of confinement in detention facilities.
Use of Force:
Incidents involving the use of force by border enforcement officers, including shootings and physical confrontations, have raised questions about the appropriate use of force policies, accountability mechanisms, and transparency in investigations of alleged misconduct.
Collaborative Approaches to Border Security
Addressing the complexities of immigration-related crimes and border security requires collaborative approaches involving multiple stakeholders:
Interagency Cooperation:
Collaboration between federal, state, and local law enforcement agencies, as well as international partners, is essential for coordinating border security efforts, sharing intelligence, and responding to transnational threats effectively.
Community Engagement:
Building trust and partnerships with border communities, immigrant advocacy organizations, and civil society groups can enhance communication, promote transparency, and foster cooperation in addressing border security challenges.
International Cooperation:
Bilateral and multilateral cooperation with neighboring countries and international organizations is critical for addressing transnational threats, such as drug trafficking, human smuggling, and terrorism, that impact border security.
Impact of Migration Policies on Communities
Migration policies, including border security measures and enforcement actions, have significant impacts on communities along the border and beyond:
Social Cohesion:
Heightened border security measures can disrupt social cohesion within border communities, leading to tensions and mistrust between residents and law enforcement authorities. Community policing efforts and outreach programs can help mitigate these tensions and build trust between law enforcement and local residents.
Economic Vitality:
Border communities often rely on cross-border trade, tourism, and labor mobility for economic vitality. Excessive border security measures and restrictions on migration can hinder economic opportunities, disrupt supply chains, and negatively impact local businesses and industries.
Cultural Exchange:
Border regions are often characterized by cultural diversity and cross-cultural exchange. Migration policies that promote dialogue, cultural exchange, and mutual understanding between neighboring communities can enrich social fabric and strengthen ties between border regions.
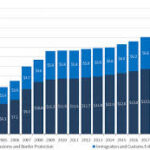
Role of Border Security in Economic and Social Dynamics
Border security measures influence economic and social dynamics at the local, regional, and national levels:
Labor Markets:
The availability of migrant labor, both authorized and unauthorized, plays a critical role in various sectors of the economy, including agriculture, construction, hospitality, and healthcare. Border security policies impact labor supply, wages, and employment opportunities in these sectors.
Social Services:
Undocumented immigrants contribute to local economies through consumption, tax revenue, and participation in community life. Policies that restrict access to social services and public benefits based on immigration status can have unintended consequences, including negative impacts on public health, education, and social welfare.
Cultural Diversity:
Immigration enriches the cultural tapestry of the United States, contributing to diversity, innovation, and creativity. Border security policies that prioritize inclusivity, diversity, and multiculturalism can foster social cohesion and strengthen social bonds within communities.
Need for Comprehensive Immigration Reform
Addressing the challenges of immigration-related crimes and border security requires comprehensive immigration reform:
Pathways to Legalization:
Creating pathways to legalization for undocumented immigrants already residing in the United States can enhance border security by incentivizing compliance with immigration laws, reducing the demand for illegal border crossings, and promoting integration and social cohesion.
Conclusion
Immigration-related crimes and border security remain complex and dynamic issues at the forefront of national debates in the United States. By adopting comprehensive and balanced approaches that integrate enforcement efforts with respect for human rights, leverage technological innovations for border surveillance, and foster collaboration among stakeholders, the US can work towards enhancing border security while upholding its values of fairness, justice, and respect for human dignity.





