Mass shootings in the United States have tragically become a recurring and deeply concerning phenomenon, sparking intense debates about gun control, mental health, and societal factors contributing to such violence. This detailed essay provides an in-depth analysis of mass shootings in the USA, exploring their prevalence, causes, impacts, and potential solutions.
Understanding Mass Shootings
Definition and Scope:
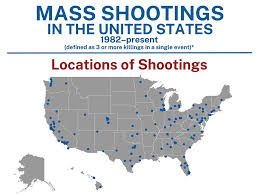
Mass shootings are typically defined as incidents in which four or more individuals are killed or injured by gunfire in a single location and time. While these events capture significant media attention, they represent only a fraction of overall gun violence in the country.
Prevalence:
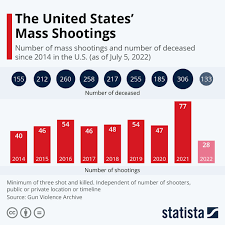
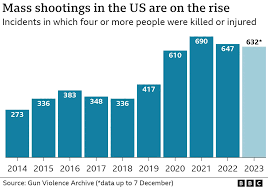
The United States experiences a disproportionately high number of mass shootings compared to other developed nations. According to data from the Gun Violence Archive, there were over 400 mass shootings in the USA in 2021 alone, resulting in hundreds of deaths and injuries.
Causes of Mass Shootings
Access to Firearms:
The widespread availability of firearms, including semi-automatic rifles and high-capacity magazines, facilitates the perpetration of mass shootings. Loopholes in gun laws, such as background check exemptions for private sales and gun show purchases, further exacerbate the issue.
Mental Health:
While mental illness is not a primary driver of mass shootings, individuals with untreated mental health issues may be more susceptible to engaging in violent behavior. However, the vast majority of people with mental illnesses are not violent, and scapegoating mental health perpetuates stigma without addressing root causes.
Cultural Factors:
Societal glorification of violence in media and popular culture, combined with toxic masculinity norms, can contribute to a culture of aggression and desensitization to violence. Additionally, social alienation and feelings of disenfranchisement may drive some individuals to seek attention or notoriety through violent acts.
Impacts of Mass Shootings
Loss of Life:
The immediate consequence of mass shootings is the tragic loss of innocent lives, causing immeasurable pain and suffering for victims’ families and communities. The trauma extends beyond physical injuries, leaving lasting psychological scars on survivors and witnesses.
Fear and Anxiety:
Mass shootings instill fear and anxiety in the general population, eroding feelings of safety and security in public spaces. This fear can have far-reaching consequences, influencing behaviors, policies, and societal attitudes toward guns and violence.
Social and Economic Costs:
Mass shootings impose significant social and economic costs, including medical expenses, law enforcement response, and lost productivity. The long-term impact on affected communities can be profound, leading to decreased property values, business closures, and decreased quality of life.
Addressing Mass Shootings: Potential Solutions
Comprehensive Gun Reform:
Implementing universal background checks, closing loopholes in existing gun laws, and banning high-capacity magazines and military-style assault weapons are critical steps in reducing the frequency and severity of mass shootings.
Investment in Mental Health Services:
Increasing access to mental health care, reducing stigma, and improving early intervention and crisis response services can help identify and support individuals at risk of engaging in violence.
Community-Based Interventions:
Investing in community-based violence prevention programs, such as conflict resolution initiatives, youth mentorship programs, and neighborhood revitalization efforts, can address root causes of violence and promote social cohesion.
Education and Awareness:
Promoting responsible gun ownership, encouraging safe storage practices, and educating the public about warning signs of potential violence can help prevent mass shootings and mitigate their impact.
Media Coverage and Copycat Phenomenon
Sensationalism:
Mass shootings often receive extensive media coverage, with sensationalized reporting focusing on the perpetrator’s motives, methods, and potential warning signs. This sensationalism can inadvertently contribute to the phenomenon by glorifying the perpetrator and inspiring copycat attacks.
Copycat Effect:
Research suggests that media coverage of mass shootings can influence subsequent acts of violence, leading to a phenomenon known as the “copycat effect.” Perpetrators may seek to emulate previous attackers in pursuit of notoriety or to amplify their grievances.
Media Guidelines:
Some experts advocate for responsible media reporting guidelines that emphasize factual accuracy, avoid sensationalizing perpetrators, and minimize graphic details of violence. Implementing such guidelines could help mitigate the risk of inspiring future attacks.
International Comparisons and Policy Implications
Global Perspective:
While mass shootings occur in other countries, the prevalence and severity of such incidents in the USA stand out in international comparisons. Countries with stricter gun control laws and comprehensive social safety nets generally experience lower rates of gun violence and mass shootings.
Policy Lessons:
Examining successful approaches to gun control and violence prevention in other countries can provide valuable insights for policymakers in the USA. Measures such as licensing requirements, mandatory waiting periods, and restrictions on firearm ownership for individuals with a history of violence or mental illness have been effective in reducing gun-related deaths in other nations.
Barriers to Reform:
Despite evidence of the effectiveness of certain policy interventions, political polarization, lobbying by gun rights advocates, and constitutional interpretations of the Second Amendment pose significant barriers to enacting comprehensive gun reform in the USA.
Intersectionality and Root Causes of Violence
Race and Gun Violence:
Gun violence disproportionately affects communities of color, with African American and Hispanic individuals experiencing higher rates of firearm-related deaths and injuries. Structural inequalities, including poverty, lack of access to quality education and healthcare, and systemic racism, contribute to this disparity.
Gender and Mass Shootings:
The intersection of gender and mass shootings is complex, with the majority of perpetrators being male. Toxic masculinity norms, feelings of entitlement, and perceptions of power and control may play a role in motivating some male perpetrators to commit acts of mass violence.
Extremism and Ideological Motivations:
Some mass shootings are motivated by extremist ideologies, including white supremacy, misogyny, and anti-government sentiments. Addressing the root causes of extremism and combating hate speech and propaganda are essential components of preventing ideologically motivated violence.
The Role of Social Media
Dissemination of Information:
Social media platforms have become powerful tools for disseminating information about mass shootings, often in real-time. While this can facilitate rapid communication and awareness, it can also contribute to misinformation, panic, and the spread of extremist ideologies.
Online Radicalization:
Extremist groups and individuals may use social media to radicalize vulnerable individuals, amplifying grievances and promoting violent ideologies. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube have faced criticism for their role in facilitating the spread of hate speech and extremist content.
Monitoring and Regulation:
Efforts to monitor and regulate online content to prevent radicalization and violence present complex challenges, including balancing freedom of speech with the need to prevent harm. Collaboration between tech companies, law enforcement agencies, and civil society organizations is essential in developing effective strategies for addressing online extremism.
Impact on Public Policy
Policy Responses:
Mass shootings often prompt calls for legislative action, leading to debates about gun control, mental health services, and school safety measures. However, political gridlock, lobbying by interest groups, and ideological divides can hinder the passage of meaningful reforms.
State and Local Initiatives:
In the absence of federal action, many states and localities have implemented their own gun control measures, such as universal background checks, red flag laws, and restrictions on assault weapons. These initiatives highlight the role of subnational governments in addressing gun violence and protecting public safety.
Election Dynamics:
Mass shootings and gun violence have become salient issues in political campaigns, influencing voter attitudes and electoral outcomes. Candidates’ positions on gun control and public safety often feature prominently in campaign rhetoric, shaping public discourse and policy priorities.
Conclusion
Mass shootings in the United States are a complex and multifaceted issue with deep-rooted causes and far-reaching consequences. While there is no single solution to prevent these tragedies, comprehensive approaches that address access to firearms, mental health, and societal factors contributing to violence are essential. By prioritizing evidence-based policies, investing in prevention and intervention strategies, and fostering a culture of safety and respect, the USA can work towards reducing the frequency and severity of mass shootings and creating safer communities for all.


