Title: Street Gangs and Urban Violence: Understanding the Complex Dynamics
Abstract:
Street gangs and urban violence have been persistent issues in many cities across the globe, posing significant challenges to community safety, social cohesion, and public health. This essay aims to delve into the multifaceted nature of street gangs, exploring their origins, characteristics, motivations, and impact on urban violence. By examining various sociological, criminological, and psychological perspectives, as well as empirical research findings, this paper seeks to provide a comprehensive understanding of the complex dynamics underlying street gangs and their relationship with urban violence. Furthermore, it discusses potential strategies for addressing and mitigating the adverse effects of street gangs on communities.
Introduction:
Street gangs and urban violence constitute critical issues that have garnered attention from scholars, policymakers, and practitioners worldwide. While street gangs have existed for centuries, their presence and influence have evolved over time, manifesting in different forms and contexts within urban landscapes.

The association between street gangs and urban violence is undeniable, with gang-related activities often contributing to crime, disorder, and social unrest in communities. Understanding the intricate interplay between street gangs and urban violence is crucial for developing effective interventions and policies aimed at promoting public safety and well-being.
Origins and Evolution of Street Gangs:
The origins of street gangs can be traced back to various historical, social, and economic factors. In many cases, street gangs emerge in disadvantaged urban neighborhoods characterized by poverty, unemployment, inadequate social services, and a lack of opportunities for youth. These environments create fertile ground for the formation of gangs as marginalized individuals seek a sense of belonging, identity, and protection within their communities. Additionally, cultural influences, peer pressure, family dynamics, and neighborhood dynamics play significant roles in shaping gang membership and behavior.
- Over time, street gangs have evolved in response to changing societal conditions, adopting new symbols, rituals, and ideologies while adapting their activities to exploit emerging opportunities.
- The proliferation of drugs, firearms, and other illicit commodities has contributed to the expansion and sophistication of gang operations, fueling violence and criminality in urban areas.
- Furthermore, advancements in communication technology and social media have transformed the dynamics of gang culture, facilitating recruitment, coordination, and conflict escalation among gang members.
Characteristics and Motivations of Street Gangs:

Street gangs exhibit diverse characteristics and motivations that reflect their complex social dynamics and organizational structures. While gangs vary in size, composition, and activities, they often share common features such as hierarchical leadership, territorial control, and group cohesion based on loyalty and solidarity. Gang members typically adhere to a set of norms, values, and codes of conduct that govern their interactions with each other and with rival groups.
- The motivations driving individuals to join street gangs are multifaceted and often interconnected.
- For some youths, gang membership offers a sense of belonging and identity, providing social support and camaraderie that may be lacking in their family or community.
- Others are drawn to gangs by the promise of status, power, and material rewards, as participating in criminal activities can offer financial opportunities and social prestige within certain subcultures.
- Moreover, factors such as peer pressure, neighborhood dynamics, exposure to violence, and limited access to legitimate avenues for success can push vulnerable individuals toward gang involvement as a means of survival or self-preservation.
Impact of Street Gangs on Urban Violence:
The presence of street gangs has profound implications for urban violence, contributing to various forms of criminal activity, interpersonal conflict, and community disruption. Gang-related violence encompasses a wide range of behaviors, including drug trafficking, extortion, robbery, assault, and homicide, all of which pose significant threats to public safety and well-being. Moreover, gang conflicts often spill over into the broader community, leading to collateral damage, fear, and social disintegration.
- The disproportionate impact of gang violence on marginalized communities exacerbates existing inequalities and undermines trust in institutions responsible for maintaining law and order.
- High rates of gang-related homicides and injuries not only result in physical harm but also inflict psychological trauma and emotional distress on affected individuals and communities.
- Furthermore, the prevalence of gang activity can stigmatize neighborhoods, deterring investment, economic development, and social cohesion.

Underlying drivers of gang-related violence:
Understanding the underlying drivers of gang-related violence is essential for developing targeted interventions and preventive strategies aimed at reducing its prevalence and impact. Research indicates that structural factors such as poverty, unemployment, lack of educational opportunities, and social disorganization contribute to the proliferation of street gangs and their involvement in violent behavior. Therefore, efforts to address gang violence must address these root causes through comprehensive approaches that encompass community development, social welfare programs, education reform, and economic revitalization.
Structural inequalities:
In addition to addressing structural inequalities, interventions targeting street gangs should focus on disrupting the social networks, economic incentives, and cultural dynamics that sustain gang activity. Law enforcement agencies can adopt strategies such as community policing, focused deterrence, and intelligence-led policing to target high-risk individuals and gang hotspots while building trust and collaboration with local residents. Moreover, multidisciplinary approaches that involve collaboration between law enforcement, social services, schools, and community organizations can provide holistic support to individuals at risk of gang involvement, offering alternatives to violence and criminality.
Conclusion:

Street gangs and urban violence represent complex social phenomena shaped by a myriad of historical, economic, cultural, and institutional factors. While the association between gangs and violence is undeniable, it is essential to recognize the underlying drivers and dynamics that fuel gang-related activities in urban communities. By adopting a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach, policymakers, practitioners, and community members can work together to address the root causes of gang violence while promoting positive alternatives for at-risk youth. Ultimately, achieving lasting solutions to the challenges posed by street gangs requires a concerted effort to address structural inequalities, strengthen social bonds, and foster inclusive and resilient communities.



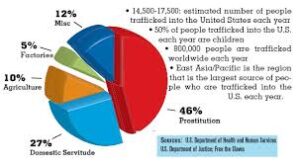
Fabulous, what a blog it is! This blog gives valuable information to us, keep it up.
http://unasoft.com.ua/termostiikyy-kley-dlya-stekla-far-yak-vybraty-naykrashchyy-variant