INTRODUCTION
Robbery is a criminal offense that involves the unlawful taking of property or valuables from an individual or establishment through force, intimidation, or threat of violence. Armed robbery and theft are two distinct but closely related forms of robbery, each with its own characteristics, methods, and legal implications. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll delve into the complexities of armed robbery and theft, examining their prevalence, motives, tactics, and impacts on individuals and communities.

1. Armed Robbery: Armed robbery is a serious criminal offense that involves the use of weapons or threats of violence to intimidate victims and steal their property. Perpetrators of armed robbery typically carry firearms, knives, or other dangerous weapons to coerce compliance and deter resistance.
2. Characteristics of Armed Robbery:
- Armed robbery is often premeditated, with perpetrators planning their actions to maximize the likelihood of success and minimize the risk of apprehension.
- Targets of armed robbery may include banks, convenience stores, gas stations, liquor stores, jewelry shops, and other businesses with cash or valuable assets.
- Perpetrators may act alone or as part of organized criminal groups, employing violence or intimidation tactics to subdue victims and gain control of the situation.
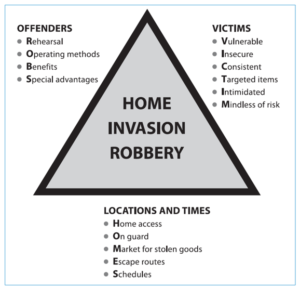
3. Methods and Tactics:
- Perpetrators of armed robbery may enter establishments during operating hours or wait until closing time to minimize the presence of witnesses and security measures.
- Common tactics used in armed robbery include brandishing weapons, issuing threats, demanding cash or valuables, and using physical force or violence against victims or bystanders.
- Getaway vehicles and accomplices may be used to facilitate escape and evade capture by law enforcement authorities.
4. Psychological Impact:
- Victims of armed robbery often experience profound psychological trauma, including fear, anxiety, helplessness, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Witnessing or experiencing violence during an armed robbery can have long-lasting effects on victims’ mental health and well-being, affecting their sense of safety, trust, and security.
5. Legal Implications:
- Armed robbery is a serious criminal offense punishable by law in most jurisdictions, with penalties ranging from imprisonment to fines and restitution.
- Aggravating factors, such as the use of firearms, injury to victims, or prior criminal history, may result in enhanced charges and sentencing under applicable statutes.
- Law enforcement agencies employ various investigative techniques, including surveillance, forensic analysis, and witness interviews, to identify and apprehend perpetrators of armed robbery.
6. Theft: Theft, also known as larceny or stealing, is the unauthorized taking of property or assets belonging to another person or entity without their consent. Unlike armed robbery, theft does not involve the use of force, violence, or threats against victims.
7. Characteristics of Theft:
- Theft can occur in various settings, including homes, businesses, public spaces, and online platforms, where perpetrators exploit opportunities to steal property or valuables.
- Common targets of theft include personal belongings, electronic devices, bicycles, motor vehicles, packages, merchandise, and financial assets.
- Perpetrators of theft may employ stealth, deception, distraction, or fraud to avoid detection and escape consequences.

8. Methods and Tactics:
- Perpetrators of theft may use various methods to commit their crimes, such as pickpocketing, shoplifting, burglary, identity theft, credit card fraud, or online scams.
- Theft may occur opportunistically, such as stealing unattended items or belongings left in plain sight, or through more sophisticated schemes involving planning and coordination.
9. Impact on Victims:
- Victims of theft may experience feelings of violation, intrusion, and vulnerability, particularly if personal or sentimental items are stolen.
- Financial losses resulting from theft can have significant repercussions for individuals and businesses, affecting their financial stability, creditworthiness, and trust in others.
10. Legal Implications:
- Theft is considered a criminal offense under the laws of most jurisdictions, with penalties ranging from fines and probation to imprisonment, depending on the value of the stolen property and the circumstances of the crime.
- Repeat offenders or individuals engaged in organized theft rings may face more severe consequences and enhanced sentencing under applicable statutes.
In conclusion, armed robbery and theft are serious crimes that pose significant threats to public safety, security, and well-being. Understanding the characteristics, methods, psychological impacts, and legal implications of these crimes is essential for preventing and addressing robbery-related incidents effectively. By implementing proactive measures, enhancing security protocols, and promoting community awareness and cooperation, stakeholders can work together to combat robbery and protect individuals and communities from harm.



