Introduction
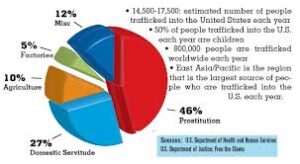
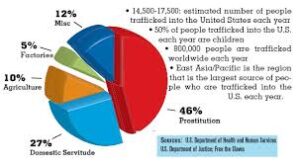
Trafficking crimes represent a grave violation of human rights and dignity, with devastating consequences for victims and communities. In the United States, trafficking encompasses various forms of exploitation, including sex trafficking, labor trafficking, and trafficking of minors. This essay explores the multifaceted nature of trafficking crimes in the USA, examining their root causes, impacts, and the strategies employed to combat them.
Understanding Trafficking Crimes

Trafficking crimes involve the recruitment, harboring, transportation, provision, or obtaining of individuals through force, fraud, or coercion for the purpose of exploitation. These crimes can occur within domestic or international contexts and may involve adults, children, and vulnerable populations. Common forms of trafficking include:
Sex Trafficking:
The recruitment, harboring, or transportation of individuals for the purpose of sexual exploitation. Victims of sex trafficking are coerced or forced into prostitution, pornography, or other forms of commercial sexual exploitation.
Labor Trafficking:
The recruitment, harboring, or transportation of individuals for the purpose of forced labor or servitude. Victims of labor trafficking may be exploited in various industries, including agriculture, construction, domestic work, manufacturing, and hospitality.
Trafficking of Minors:
The exploitation of children for commercial sex or labor purposes. Minors are particularly vulnerable to trafficking due to their age, dependency, and susceptibility to manipulation and coercion.
Root Causes of Trafficking Crimes Trafficking crimes are driven by a complex interplay of economic, social, and structural factors. Root causes include:
Poverty and Economic Inequality:
Economic disparities and lack of opportunity create vulnerabilities that traffickers exploit. Individuals from marginalized communities, impoverished regions, and unstable socio-economic backgrounds are at higher risk of trafficking due to their economic desperation.
Demand for Cheap Labor and Services:
The demand for cheap labor and services in industries such as agriculture, construction, and hospitality fuels labor trafficking. Employers may exploit undocumented immigrants or vulnerable workers by subjecting them to exploitative working conditions and low wages.
Gender Inequality and Discrimination:
Gender-based discrimination and patriarchal norms contribute to the prevalence of sex trafficking. Women and girls are disproportionately targeted for sexual exploitation, often lured into trafficking through false promises of employment, education, or marriage.
Social Vulnerability and Marginalization:
Individuals facing social isolation, homelessness, substance abuse, mental illness, or involvement in the child welfare system are at heightened risk of trafficking. Traffickers prey on vulnerable populations, exploiting their vulnerabilities for profit.
Impacts of Trafficking Crimes Trafficking crimes have profound and enduring impacts on victims, survivors, and society as a whole. The impacts include:
Physical and Psychological Trauma:
Victims of trafficking endure physical violence, sexual abuse, and psychological coercion, leading to profound trauma and long-term psychological harm. Survivors may suffer from PTSD, depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders as a result of their exploitation.
Loss of Freedom and Autonomy:
Trafficking victims are deprived of their fundamental rights and freedoms, including the right to liberty, autonomy, and self-determination. They may be subjected to physical confinement, isolation, and threats of violence to maintain control over them.

Health Consequences:
Trafficking victims face a range of health consequences, including untreated medical conditions, reproductive health issues, and exposure to sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and HIV/AIDS. Limited access to healthcare and reproductive services further exacerbates their health vulnerabilities.
Stigmatization and Social Exclusion:
Trafficking survivors often face stigma, shame, and social ostracism, hindering their reintegration into society. The stigma associated with trafficking can perpetuate cycles of victimization and prevent survivors from seeking help and support.
Responses to Trafficking Crimes Addressing trafficking crimes requires a comprehensive and multi-sectoral approach that involves prevention, protection, prosecution, and partnerships. Strategies for combating trafficking include:
Legislative Frameworks and Legal Protections:
Enacting and enforcing robust anti-trafficking laws at the federal, state, and local levels. Legislative measures should criminalize trafficking offenses, enhance penalties for perpetrators, and provide legal protections and support services for victims and survivors.
Victim-Centered Approaches:
Prioritizing the needs and rights of trafficking victims through trauma-informed and survivor-centered approaches. Providing comprehensive services, including shelter, medical care, counseling, legal assistance, and case management, to support victims’ recovery and empowerment.

Awareness and Education:
Raising public awareness about the realities of trafficking and its impact on individuals and communities. Education campaigns, training programs, and outreach initiatives help identify and prevent trafficking, promote reporting, and challenge myths and misconceptions.
International Cooperation and Collaboration:
Strengthening international partnerships and cooperation to combat trafficking across borders. Collaboration with foreign governments, law enforcement agencies, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) is essential to disrupt trafficking networks, rescue victims, and prosecute perpetrators.
Corporate Responsibility and Supply Chain Transparency:
Holding businesses and industries accountable for preventing and addressing trafficking within their supply chains. Implementing responsible sourcing practices, conducting due diligence on suppliers, and supporting ethical labor standards help prevent labor trafficking and exploitation.
Conclusion

Trafficking crimes represent a grave violation of human rights and dignity, with profound and enduring consequences for victims and survivors. By understanding the root causes of trafficking, addressing vulnerabilities, and implementing effective responses, the USA can work towards preventing trafficking, protecting victims, and holding perpetrators accountable. Through collaborative efforts among governments, law enforcement agencies, civil society organizations, and communities, we can create a future where trafficking crimes are eradicated, and all individuals can live free from exploitation and abuse.