Introduction
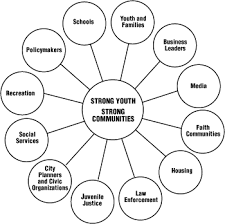
Youth crime prevention and needs assessment are crucial aspects of addressing juvenile delinquency and promoting the well-being of young people. Here’s a general overview of these topics:
Youth Crime Prevention
This involves implementing strategies and programs aimed at reducing the likelihood of young people engaging in criminal behavior. Prevention efforts often focus on addressing risk factors associated with delinquency while also promoting protective factors that contribute to positive youth development. Prevention strategies may include:
Early intervention programs:
Identifying and intervening in the lives of at-risk youth at an early age to prevent further involvement in criminal activities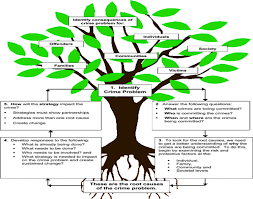
Community-based programs
Offering after-school programs, mentorship initiatives, recreational activities, and educational opportunities to keep young people engaged in positive activities.
Family support services
Providing support to families to strengthen parent-child relationships, improve parenting skills, and address family-related risk factors.
School-based interventions
Implementing anti-bullying programs, conflict resolution training, and other initiatives to create a positive and safe school environment.
Youth empowerment initiatives
Encouraging youth participation in decision-making processes, promoting leadership skills, and providing opportunities for civic engagement.
Needs Assessment
Conducting a needs assessment involves identifying the specific needs and challenges faced by youth in a particular community or population. This assessment helps in developing targeted interventions and allocating resources effectively. Key steps in a needs assessment process may include:
Data collection
Gathering information through surveys, interviews, focus groups, and existing data sources to understand the demographics, risk factors, and service gaps within the youth population.
Analysis
Analyzing the collected data to identify patterns, trends, and areas of concern related to youth behavior, socio-economic conditions, access to resources, etc.
Stakeholder engagement
Involving key stakeholders such as youth, parents, educators, law enforcement, community leaders, and service providers in the assessment process to gain diverse perspectives and insights.
Prioritization
Prioritizing needs based on their urgency, impact, and feasibility of intervention.
Action planning
Developing strategies and action plans to address identified needs, including setting specific goals, outlining intervention approaches, and determining resource allocation.
Monitoring and evaluation
Continuously monitoring the implementation of interventions and evaluating their effectiveness in addressing the identified needs, making adjustments as necessary.
By combining effective youth crime prevention strategies with thorough needs assessments, communities can better support the positive development of young people and reduce their involvement in criminal activities.
Certainly! Let’s delve deeper into the process of youth crime prevention and needs assessment:
1. Understanding the Context:
Demographics
Gather data on the age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status of the youth population in the community.
Crime Data
Analyze local crime statistics to identify trends in youth involvement in criminal activities, such as types of offenses committed, locations, and times of occurrence.
Community Resources
Identify existing resources available to youth, including schools, recreational facilities, mental health services, and youth organizations.
Environmental Factors
Consider environmental influences such as neighborhood safety, access to parks and community centers, and the prevalence of gangs or drug activity.
2. Identifying Risk and Protective Factors: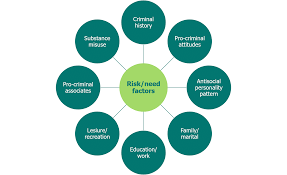
Risk Factors
Common risk factors for youth involvement in crime include poverty, lack of parental supervision, academic failure, peer pressure, substance abuse, and exposure to violence.
Protective Factors
Protective factors that buffer against involvement in delinquent behavior include strong family relationships, positive adult role models, access to education and employment opportunities, and community support networks.
3. Needs Assessment:

Data Collection:
Use a variety of methods to gather information, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, and analysis of existing data sources such as school records, police reports, and social service records.
Youth Input:
Ensure the active participation of youth in the needs assessment process by soliciting their input through surveys, focus groups, and youth-led discussions.
Identifying Gaps
Identify gaps in services and resources for youth, as well as unmet needs or challenges they face, such as mental health issues, substance abuse, lack of positive role models, or barriers to accessing education and employment.
4. Stakeholder Engagement:
Collaboration
Engage a diverse range of stakeholders, including youth, parents, educators, law enforcement, social service agencies, local government, and community organizations.
Partnerships
Foster partnerships and collaborations between stakeholders to leverage resources, share expertise, and coordinate efforts in addressing youth crime and promoting positive youth development.
5. Developing Prevention Programs:
Evidence-Based Practices
Base prevention programs on evidence-based practices that have been shown to effectively reduce youth crime and delinquency.
Tailored Interventions
Tailor interventions to address the specific needs and risk factors identified during the needs assessment process.
Holistic Approach
Adopt a holistic approach that addresses multiple risk and protective factors simultaneously, rather than focusing on individual behaviors in isolation.
Implementation Plan
Develop a detailed plan for implementing prevention programs, including timelines, roles and responsibilities, and strategies for outreach and engagement.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of prevention efforts through process evaluation, outcome evaluation, and impact assessment.
Feedback and Adaptation
Solicit feedback from stakeholders and participants to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to the program as needed.
7. Sustainability and Long-term Planning:
Funding Strategies:
Identify sustainable funding sources to support ongoing prevention efforts, such as government grants, private donations, and partnerships with local businesses and philanthropic organizations.
Capacity Building:
Build capacity within the community by training local stakeholders, developing leadership skills among youth, and fostering collaboration between agencies and organizations.
Strategic Planning:
Develop a long-term strategic plan for youth crime prevention that outlines goals, objectives, and strategies for addressing emerging challenges and adapting to changing needs over time.
By following these steps and adopting a comprehensive approach to youth crime prevention and needs assessment, communities can effectively address the underlying factors that contribute to juvenile delinquency and promote the well-being and positive development of young people.
In conclusion,
by implementing evidence-based prevention strategies that address the complex interplay of social, economic, and environmental factors influencing youth crime, we can create safer and more resilient communities for future generations. Preventing youth crime requires a long-term commitment and a concerted effort from all sectors of society, but the benefits of investing in our youth’s future are immeasurable.Youth crime prevention is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a holistic approach involving various stakeholders including families, communities, educators, law enforcement agencies, and policymakers. In conclusion, effective strategies for preventing youth crime should focus on several key areas:


