Substance abuse and its correlation with crime in the USA constitute a significant public health and criminal justice concern. This essay provides a detailed analysis of the relationship between substance abuse and crime, exploring the underlying causes, impacts on individuals and society, and potential solutions to address this complex issue.
Understanding the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Crime
Defining Substance Abuse:
Substance abuse refers to the harmful or hazardous use of psychoactive substances, including drugs and alcohol, which can lead to addiction, impaired judgment, and negative health outcomes.
Types of Crimes Associated with Substance Abuse:
Substance abuse is linked to various types of criminal behavior, including drug-related offenses (possession, trafficking), property crimes (theft, burglary), violent crimes (assault, homicide), and offenses committed under the influence of alcohol or drugs (DUI).
Complex Interplay:
The relationship between substance abuse and crime is multifaceted, with substance abuse serving as both a cause and consequence of criminal behavior. Individuals may turn to substance abuse as a coping mechanism for underlying social, economic, or psychological stressors, while the intoxicating effects of drugs and alcohol can impair judgment and increase the likelihood of engaging in criminal activity.
Causes of Substance Abuse and Crime
Biological Factors:
Genetic predispositions and neurological vulnerabilities may increase susceptibility to substance abuse disorders, which can manifest in impulsive or reckless behavior conducive to criminal activity.
Environmental Influences:
Socioeconomic factors such as poverty, unemployment, lack of access to education, and exposure to violence contribute to the prevalence of substance abuse and crime in disadvantaged communities. Limited economic opportunities and social support systems may drive individuals to illicit means of obtaining drugs or alcohol.
Psychological Factors:
Co-occurring mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and trauma-related disorders, often coexist with substance abuse and increase the risk of involvement in criminal behavior. Substance abuse may serve as a maladaptive coping mechanism for individuals struggling with untreated mental health issues.

Impacts of Substance Abuse-Related Crime
Individual Consequences:
Substance abuse-related crime can have devastating consequences for individuals, including arrest, incarceration, and long-term involvement in the criminal justice system. The stigma associated with criminal records may hinder employment opportunities and access to housing and social services, perpetuating cycles of poverty and recidivism.
Community Effects:
Substance abuse-related crime contributes to community instability, erodes trust in law enforcement, and strains resources for social services and healthcare. High crime rates in neighborhoods plagued by substance abuse can deter economic development and compromise residents’ quality of life.
Economic Burden:
The societal costs of substance abuse-related crime are substantial, encompassing expenses related to law enforcement, judicial proceedings, incarceration, and victim services. Additionally, productivity losses due to substance abuse-related absenteeism, disability, and premature death impose significant economic burdens on society.
Addressing Substance Abuse-Related Crime: Potential Solutions
Prevention and Early Intervention:
Investing in evidence-based prevention programs that target at-risk populations, including youth and individuals with co-occurring disorders, can mitigate the onset of substance abuse and reduce the likelihood of involvement in criminal behavior.
Treatment and Rehabilitation:
Access to comprehensive substance abuse treatment and rehabilitation services, including medication-assisted therapy, counseling, and vocational training, is essential for individuals struggling with substance use disorders. Alternative sentencing programs, such as drug courts and diversion programs, can provide non-carceral interventions for low-level offenders with substance abuse issues.
Harm Reduction Strategies:
Implementing harm reduction strategies, such as needle exchange programs, supervised injection sites, and naloxone distribution, can reduce the adverse health consequences of substance abuse and minimize the risk of overdose deaths.
Community Policing and Collaboration:
Adopting community policing approaches that emphasize collaboration between law enforcement, social service agencies, healthcare providers, and community organizations can foster trust, improve communication, and address the root causes of substance abuse-related crime.
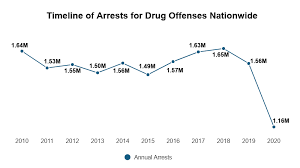
Impact of Specific Substances
Opioid Epidemic:
The opioid epidemic has had a profound impact on substance abuse and crime in the USA. Prescription opioid misuse often leads to addiction, with individuals resorting to illegal means, such as doctor shopping or purchasing opioids on the black market, to sustain their addiction. Additionally, the rise in heroin and fentanyl use has contributed to increased rates of overdose deaths and drug-related crimes.
Stimulants and Methamphetamine:
The misuse of stimulants, such as methamphetamine and cocaine, is associated with heightened aggression, paranoia, and impulsive behavior, leading to an increased risk of violent crime and property crimes. Methamphetamine production and distribution networks also pose significant challenges for law enforcement agencies.
Alcohol and Violent Crime:
Alcohol remains one of the most commonly abused substances in the USA and is closely linked to violent crime. Intoxication diminishes inhibitions and impairs judgment, increasing the likelihood of aggressive behavior and interpersonal violence. Alcohol-related crimes often occur in social settings, such as bars and parties, where alcohol consumption is prevalent.
Role of Policy and Law Enforcement
Drug Policy:
The enforcement of drug laws, particularly those targeting illicit substances, has significant implications for substance abuse-related crime. The approach to drug policy, whether focused on prohibition and punishment or harm reduction and treatment, shapes the criminal justice response to substance abuse issues.
Mass Incarceration:
The “War on Drugs” and mandatory minimum sentencing laws have contributed to the disproportionate incarceration of individuals with substance abuse disorders, particularly from marginalized communities. Mass incarceration exacerbates social inequalities, disrupts families, and perpetuates cycles of poverty and crime.
Diversion Programs and Specialty Courts:
Diversion programs, including drug courts, mental health courts, and veteran courts, offer alternatives to incarceration for individuals with substance abuse issues. These programs emphasize rehabilitation, accountability, and access to treatment and support services, aiming to address underlying factors contributing to criminal behavior.
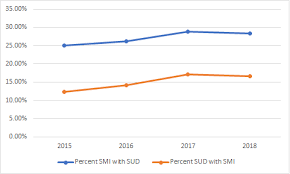
Challenges and Opportunities in Addressing Substance Abuse-Related Crime
Stigma and Discrimination:
Stigma surrounding substance abuse and addiction can deter individuals from seeking help and accessing treatment services. Addressing stigma requires education, advocacy, and destigmatization efforts to promote empathy, understanding, and support for individuals struggling with substance use disorders.
Access to Treatment:
Disparities in access to substance abuse treatment services, particularly in rural and underserved areas, present significant challenges. Increasing funding for treatment programs, expanding Medicaid coverage for substance abuse treatment, and integrating mental health and addiction services can improve access and reduce barriers to care.
Intersectionality and Equity:
Substance abuse-related crime disproportionately affects marginalized communities, including people of color, LGBTQ+ individuals, and those experiencing homelessness or poverty. Addressing structural inequalities, addressing trauma and social determinants of health, and promoting equity in the delivery of services are essential components of an effective response.
Conclusion
Substance abuse and crime in the USA are deeply intertwined phenomena with complex social, economic, and psychological dimensions. Addressing the root causes of substance abuse-related crime requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses prevention, treatment, harm reduction, and community collaboration. By investing in evidence-based interventions, promoting social and economic opportunities, and fostering supportive environments for individuals in need, society can work towards reducing the prevalence and impact of substance abuse-related crime, ultimately promoting public safety and well-being for all.


