Title: Elder Abuse in the USA: Understanding Prevalence, Causes, Impacts, and Prevention Strategies
Abstract:
Elder abuse, a pervasive and often hidden form of mistreatment, poses significant risks to the health, safety, and well-being of older adults in the United States. This essay provides a comprehensive examination of elder abuse in the USA, exploring its prevalence, forms, risk factors, impacts, and prevention strategies. Drawing on empirical research, case studies, and policy analyses, this essay sheds light on the complex dynamics of elder abuse, including physical, emotional, financial, and neglectful forms of mistreatment. By analyzing societal attitudes, cultural factors, and systemic barriers, it highlights the urgent need for multidisciplinary approaches to address elder abuse and safeguard the rights and dignity of older adults.
Keywords: Elder Abuse, Older Adults, Prevalence, Risk Factors, Impacts, Prevention Strategies, USA
-
Introduction
Elder abuse, defined as intentional or neglectful acts that cause harm or risk of harm to older adults, is a widespread and complex issue that affects millions of individuals in the United States. Despite growing recognition of elder abuse as a serious public health and human rights concern, it remains vastly underreported and inadequately addressed. This essay provides a comprehensive examination of elder abuse in the USA, examining its prevalence, forms, risk factors, impacts, and prevention strategies. By analyzing empirical research, case studies, and policy initiatives, it seeks to raise awareness of elder abuse, promote understanding of its multifaceted nature, and foster collective action to protect older adults from harm.

-
Prevalence of Elder Abuse
Physical Abuse:
Physical abuse involves the use of force, violence, or restraint to inflict pain, injury, or impairment on an older adult. Studies suggest that physical abuse affects a significant proportion of older adults in the USA, with estimates ranging from 1% to 10% of the population.
Emotional Abuse:
Emotional or psychological abuse refers to verbal or non-verbal behaviors that cause distress, fear, or mental anguish in an older adult. Research indicates that emotional abuse is prevalent among older adults, with insults, threats, and intimidation being common forms of mistreatment.
Financial Exploitation:
Financial exploitation involves the unauthorized or improper use of an older adult’s financial resources for personal gain or fraudulent purposes. Studies suggest that financial exploitation is widespread, affecting up to 1 in 10 older adults in the USA, with losses totaling billions of dollars annually.
Neglect:
Neglect occurs when caregivers fail to provide essential care or meet the basic needs of an older adult, such as food, shelter, medical care, or personal hygiene. Neglect is one of the most common forms of elder abuse, affecting a significant proportion of older adults who rely on caregivers for assistance.
-
Risk Factors for Elder Abuse
Caregiver Stress:
Caregiver stress and burnout are significant risk factors for elder abuse, as overwhelmed caregivers may resort to abusive or neglectful behaviors due to lack of support, resources, or coping strategies.
Dependency and Vulnerability:
Older adults who are dependent on others for care, financial support, or social interaction are at increased risk of elder abuse, as they may be perceived as easy targets for exploitation or mistreatment.
Social Isolation:
Social isolation and loneliness increase the risk of elder abuse, as isolated older adults may lack social networks, support systems, or opportunities to seek help or report abuse.
Cognitive Impairment:
Older adults with cognitive impairments, such as dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, are particularly vulnerable to elder abuse, as they may have difficulty recognizing or reporting mistreatment and may be more susceptible to manipulation or coercion.
-
Impacts of Elder Abuse
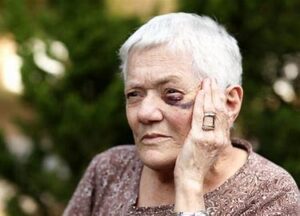
Physical Health Effects:
Elder abuse can have profound physical health consequences, including injuries, disabilities, chronic pain, and exacerbation of existing medical conditions. Physical abuse and neglect can lead to serious injuries, hospitalizations, and long-term impairments in older adults.
Psychological and Emotional Effects:
Elder abuse can cause significant psychological and emotional distress in older adults, including anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and diminished quality of life. Emotional abuse and financial exploitation can erode older adults’ self-esteem, confidence, and sense of security.
Financial Consequences:
Financial exploitation can have devastating financial consequences for older adults, including loss of savings, assets, and property, as well as financial dependence on perpetrators. Older adults may experience financial hardship, debt, and poverty as a result of exploitation and fraud.
Societal Costs:
Elder abuse imposes substantial societal costs, including healthcare expenditures, legal expenses, and social service interventions. The financial burden of elder abuse extends beyond individual victims to families, communities, and taxpayers, highlighting the importance of prevention and intervention efforts.
-
Prevention Strategies
Public Awareness Campaigns: Public education campaigns aimed at raising awareness of elder abuse, promoting recognition of warning signs, and encouraging reporting are essential for preventing and addressing mistreatment of older adults. Campaigns should target older adults, caregivers, professionals, and the general public to promote understanding and action.
Multidisciplinary Interventions: Multidisciplinary approaches to elder abuse prevention involve collaboration among healthcare providers, social workers, law enforcement, legal professionals, and community organizations to identify, intervene, and support victims of elder abuse. Coordinated efforts are essential for addressing the complex needs of older adults and ensuring timely interventions.

Capacity Building: Building capacity among professionals and service providers to recognize, respond to, and prevent elder abuse is crucial for enhancing the effectiveness of prevention efforts. Training programs, resources, and guidelines should be developed to equip professionals with the knowledge, skills, and tools needed to address elder abuse in diverse settings.
Policy and Legislative Reforms: Policy and legislative reforms are needed to strengthen legal protections, enhance enforcement mechanisms, and promote accountability for elder abuse perpetrators. Legislation should prioritize elder rights, strengthen reporting requirements, and impose penalties for offenders to deter mistreatment and promote justice for victims.
-
Conclusion
Elder abuse in the USA represents a serious public health, social, and human rights issue that demands urgent attention and action. By raising awareness, understanding risk factors, and implementing prevention strategies, stakeholders can work together to protect older adults from harm and promote their safety, dignity, and well-being. Addressing elder abuse requires a comprehensive and coordinated approach that involves individuals, families, communities, governments, and organizations working together to prevent mistreatment, support victims, and promote age-friendly environments that respect and value older adults.


